Preferences: Difference between revisions
imported>Taktik (→Keys) |
No edit summary |
||
| (87 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Preferences = | = Preferences = | ||
The | The Renoise Preferences panel lets you set various general options for the program, such as soundcard settings, MIDI device settings, how files are loaded/saved etc. These settings need to be set only once and will be applied to all songs and sounds you create with Renoise. | ||
To open the | To open the Preferences panel, choose ''"Edit -> Preferences..."'' from the main menu (Windows + Linux). On the Mac, choose ''"Renoise -> Preferences..."''. | ||
When setting up Renoise for the first time, you should only need to tweak the options in the Audio and MIDI tabs. The rest of the default options should be sufficient until you are more familiar with Renoise. The [[Setting Up Audio Devices]] and [[Setting Up MIDI Devices]] sections of the manual can help you with the initial setup. | |||
== Audio == | == Audio == | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:3.4_preferences-audio.png]] | ||
=== Device Settings (Windows) === | === Device Settings (Windows) === | ||
* '''Device Type:''' Determines the sound driver that Renoise will use. On Windows you will have the choice between DirectSound, WASAPI and ASIO. If available, ASIO is highly recommended as it provides better timing with MIDI instruments and lower latencies in general. | |||
* '''In Device''' | * '''In Device:''' ''(DirectSound only)'' If you have multiple soundcards installed, you will be able to select the one you want to use with Renoise here. Choose ''"Primary Device"'' to use the system's default. | ||
* '''Out Device''' | * '''Out Device:''' ''(DirectSound only)'' If you have multiple soundcards installed, you will be able to select the one you want to use with Renoise here. Choose ''"Primary Device"'' to use the system's default. | ||
* '''Sample Rate''' Select the | * '''Sample Rate:''' Select the Sample Rate for playback. All internal audio processing in Renoise will be done at this rate. The higher the Sample Rate, the more detailed the results will be, but also the more CPU power will be used. | ||
* '''Latency''' (DirectSound only) | * '''Latency:''' ''(DirectSound only)'' Set the buffer size affecting overall latency. Higher numbers will reduce the possibility of crackling sound at high CPU usage, but will also cause more latency (the time it takes the sound from Renoise to reach an output and be heard). | ||
* ''' | * '''Sync offset:''' A custom offset applied when [[Transport_Panel#Song_Parameters|synchronizing audio playback to an external source such Ableton Link peers]]. It is only necessary to set this if Renoise cannot reliably detect the actual output latency of the audio device. | ||
* '''Reinitialize''' Shut down and reopen all connections to the soundcard/driver. | * '''Use hardware buffers:''' ''(DirectSound only)'' This option may speed up playback processing a bit, but only some soundcards support this. If you enable this option, then experiment with recording in the [[Waveform#Recording New Samples|Sampler]] before deciding to use it permanently, as it may cause issues. If you experience strange results then disable this function. | ||
* '''Limit to stereo in/out:''' ''(ASIO only)'' If you have a multi-IO soundcard, you can disable all inputs and outputs except for the main stereo pair. This may lead to better performance when you don't need the other channels. | |||
* '''Dithering:''' Apply dithering to the audio stream when the soundcard uses a bit depth of 8 or 16 bit. 24 and 32 bit audio is never dithered. | |||
* '''Control Panel:''' ''(ASIO only)'' Opens the ASIO driver's control panel where you can configure your soundcard in more detail. | |||
* '''Reinitialize:''' Shut down and then reopen all connections to the soundcard/driver. May be useful for troubleshooting. | |||
=== Device Settings (MacOS) === | |||
* '''In Device:''' If you have multiple soundcards installed, you will be able to select the one you want to use with Renoise here. | |||
* '''Out Device:''' If you have multiple soundcards installed, you will be able to select the one you want to use with Renoise here. | |||
* '''Sample Rate:''' Select the Sample Rate for playback. All internal audio processing in Renoise will be done at this rate. The higher the Sample Rate, the more detailed the results will be, but also the more CPU power will be used. | |||
* '''Latency:''' Set the buffer size affecting overall latency. Higher numbers will reduce the possibility of crackling sound at high CPU usage, but will also cause more latency (the time it takes the sound from Renoise to reach an output and be heard). | |||
* '''Dithering:''' Apply dithering to the audio stream when the soundcard uses a bit depth of 8 or 16 bit. 24 and 32 bit audio is never dithered. | |||
* '''Reinitialize:''' Shut down and then reopen all connections to the soundcard/driver. May be useful for troubleshooting. | |||
=== Device Settings (Linux) === | === Device Settings (Linux) === | ||
Setting up Linux for fast and reliable audio usage can be quite complex, depending on the distribution you are using. For general questions and FAQs regarding sound output on Linux, take a look at the [[Linux FAQ]]. | |||
* '''Device Type:''' Determines the sound driver that Renoise will use. On Linux you have the choice between ALSA and Jack. ALSA will be available on all setups. Jack is more advanced, but also harder to set up and may have to be installed manually. Jack is highly recommended though, because it allows you to use several Jack based audio applications at once with the ability to route audio between them. | |||
* '''In Device:''' | |||
** '''ALSA:''' If you have multiple soundcards installed, you will be able to select the one you want to use with Renoise here. | |||
** '''Jack:''' Select the number of input pairs you would like to pass over to Jack. | |||
* '''Out Device:''' | |||
** '''ALSA:''' If you have multiple soundcards installed, you will be able to select the one you want to use with Renoise here. | |||
** '''Jack:''' Select the number of output pairs you would like to pass over to Jack. | |||
* '''Sample Rate:''' ''(ALSA only)'' Select the Sample Rate for playback. All internal audio processing in Renoise will be done at this rate. The higher the Sample Rate, the more detailed the results will be, but also the more CPU power will be used. | |||
* '''Buffer Size:''' ''(ALSA only)'' The base buffer size that will be used for audio processing in Renoise. Higher numbers will reduce the possibility of crackling sound at high CPU usage, but will also cause more latency (the time it takes the sound from Renoise to reach an output and be heard). | |||
* '''Periods/Buffer:''' ''(ALSA only)'' How many ''"Buffer Sizes"'' will be used. The final latency for ALSA playback is: '''''Periods/Buffer'' * ''Buffer Size'''''. Some drivers need three buffers to work reliably, while others need only two. If you hear crackling output from Renoise, try changing this value or the setting for ''"In Device"''. | |||
* '''Use realtime priority:''' ''(ALSA only)'' On most 'out of the box' Linux systems, applications are not allowed to execute realtime performance critical tasks. They are needed for realtime audio processing though, so they should be enabled when possible. Please see the [[Linux FAQ]] for more info about this topic. If you cannot configure your system to allow realtime tasks, then you can disable Renoise from trying with this option. | |||
* '''Enable Transport Support:''' ''(Jack only)'' Send and receive time and transport information to/from other applications that are running with Jack. This is only useful to sync multiple audio applications together. If you are only running Renoise, this option should be disabled. | |||
* '''Dithering:''' Apply dithering to the audio stream when the soundcard uses a bit depth of 8 or 16 bit. 24 and 32 bit audio is never dithered. | |||
* '''Reinitialize:''' Shut down and then reopen all connections to the soundcard/driver. May be useful for troubleshooting. | |||
=== Multi CPU/Core support === | === Multi CPU/Core support === | ||
* ''' | |||
* '''Realtime Audio CPUs:''' If you have a processor with multiple CPUs or cores, you can adjust how Renoise makes use of them for real-time audio processing. By default, all cores are used, which is highly recommended. | |||
=== Automatic PDC === | === Automatic PDC === | ||
* '''Automatic | |||
* '''Automatic Plugin Delay Compensation:''' This automatically compensates all delays that some Renoise internal effects and VST/AU plugins introduce. Used to ensure all tracks and instruments are played back in sync. If you are troubleshooting, you may want to temporarily disable this option. The Automatic PDC can also be quickly toggled from the [[Introduction_To_Renoise#Upper_Status_Bar|Options menu]]. | |||
=== CPU Load and Threshold === | === CPU Load and Threshold === | ||
* '''When the CPU is above, For at least:''' - When the conditions are fulfilled, Renoise executes Panic (instantly stops all playback). This option prevents very high CPU loads from freezing your computer. | |||
* ''' | |||
== MIDI == | == MIDI == | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:3.4_preferences-midi.png]] | ||
=== MIDI Master Keyboard/Mapping === | |||
* '''In Device A/B/C/D:''' Select up to four devices to be used for general MIDI input in Renoise ([[Recording and Editing Notes]]) and for MIDI remote control ([[MIDI Mapping]]). | |||
* '''In | * '''Auto-rescan when hot-plugging devices:''' When enabled and devices are hot-plugged, rescan for MIDI devices in Renoise too, so they can be immediately used. | ||
* '''Record and | * '''Rescan:''' Manually rescan MIDI devices. | ||
* '''Ignore specific controllers''' Explicitly prevent certain MIDI Control Change messages from being received and recorded. You can enter a list of CC numbers here, separated by commas. | * '''Record and Play Filters:''' Toggle the input and recording of [[MIDI#MIDI_Messages|specific MIDI messages]] for Renoise. This only applies to recording into patterns and real-time playback. | ||
* '''Adjust recording latency:''' Will automatically compensate for MIDI latencies, so that you record what you hear, not what you play. | |||
* '''Fix received MIDI event jitter:''' Shifts received MIDI events slightly forward in time to fix MIDI transmission jitter. Stabilizes MIDI input, but also delays input by an entire audio buffer. | |||
* '''Ignore specific controllers:''' Explicitly prevent certain MIDI Control Change messages from being received and recorded. You can enter a list of CC numbers here, separated by commas. | |||
=== MIDI Clock Master === | === MIDI Clock Master === | ||
=== | * '''Out Device:''' Set a MIDI device that Renoise will send MIDI Clock data to. | ||
* '''In-Device''' | * '''Offset:''' Manually shift all messages sent out to the devices by the given amount. This can be useful to manually compensate additional latencies that external devices introduce (audio latency is always automatically compensated by Renoise). Please note that the smallest possible negative latency is limited to the current latency of your soundcard. If you need further negative latency, you can increase your audio latency in the [[Preferences#Audio|Audio Preferences]]. | ||
* '''Offset''' Manually shift incoming timing information by the given amount. This can be useful to manually compensate extra latencies that the | * '''Send clock:''' Include sending MIDI Clock pulse messages. | ||
* '''Smoothing''' MIDI messages often have | * '''Send start/stop:''' Include sending MIDI Clock start/stop messages. | ||
* '''Send song position pointers:''' Include sending MIDI Clock song position messages. | |||
* '''Send MIDI Machine Control (MMC):''' In addition to the MIDI clock, also send MMC sysex messages to sync external devices to Renoise. | |||
=== MIDI Clock Slave === | |||
* '''In-Device:''' Select the MIDI Device that Renoise will use to receive MIDI Clock messages. When enabled, you can slave Renoise to a MIDI Clock master (a device which sends MIDI Clock messages). As soon as a MIDI Clock device is set, you will see a new option in the [[Transport Panel]]. This option must be enabled to activate sync from external devices and so can also be used to toggle sync quickly without having to constantly open the Preferences. | |||
* '''Offset:''' Manually shift incoming timing information by the given amount. This can be useful to manually compensate extra latencies that the external MIDI Clock devices introduce (audio latency is always automatically compensated by Renoise). Since Renoise can't predict the future, a negative latency setting will lead to the offset being gradually shifted to its requested position after playback starts. | |||
* '''Smoothing:''' MIDI messages often only have very rough timing, so the beat clock messages transferred from a MIDI Clock master to Renoise may be imperfect. Depending on how precise the incoming MIDI clock stream is, you can use this option to set how fast Renoise should react to changes from the MIDI Clock master. The higher the Smoothing value, the more stable the sync will be, but the slower Renoise will react to 'real' BPM changes from the master. Try playing around with the Smoothing to find a good value for your setup. | |||
== OSC == | |||
[[Image:3.3_preferences-osc.png]] | |||
=== Server === | |||
The server is enabled with the checkbox near the top, though note that you are opening up a port that is listening for incoming traffic. If you are not planned to use OSC messaging between Renoise and another OSC client, it is advisable to leave the OSC server disabled. Beneath the checkbox is the messaging log window, which shows details of any incoming data and provides feedback on whether outgoing data has been sent correctly or otherwise. | |||
* '''Protocol:''' Choose from UDP (for local network and anything with a fast, stable connection) or TCP (for remote networks requiring more secure feedback on delivery status). | |||
* '''Port:''' The port number, which by default is 8000, but can be changed to any desired port. | |||
=== Renoise OSC Messaging Protocols === | |||
Renoise provides four sub-trees in its root messaging tree of /renoise/: | |||
* '''evaluate''' - Send Lua strings for Renoise to evaluate. | |||
* '''song''' - Send song specific triggers to activate. | |||
* '''transport''' - Send transport specific triggers to activate. | |||
* '''trigger''' - Send note specific triggers to activate. | |||
For full details of using OSC within Renoise, please refer to [[Open_Sound_Control|its section of the manual.]] | |||
== Files == | == Files == | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:3.3_preferences-files.png]] | ||
'''Note:''' All import options mentioned below can also be quickly accessed in the [[Disk Browser]] by right-clicking the file, then choosing ''"Load File with Options..."'' | |||
=== WAV Import === | |||
Applies to WAV, FLAC, AIF, OGG and MP3 files. | |||
* '''Import loop settings from files:''' Enables the importing of loop settings that are saved along with WAV, FLAC and AIF files. | |||
* '''Autoset 'Beatsync' length:''' When loading samples, a good Beatsync value will be automatically estimated in the [[Sampler#Sample Properties|Sample Properties]], overwriting previous values. If you don't want this to happen, disable it here. | |||
=== Raw Audio Import === | |||
Applies to any non-audio files that are forced to be loaded as audio. See [[Disk_Browser#Importing_Raw_Audio_Files_(Convert_Any_File_to_Audio_Sample)|Importing Raw Audio]] for more details. | |||
* '''Bits:''' Bit-rate that will be applied to the imported raw sample. | |||
* '''Sample Rate:''' Sample rate of raw samples. | |||
* '''Skip header bytes:''' Will skip the specified number of bytes and not treat them as audio data. | |||
* '''Big Endian:''' Select the byte order that will be used for the raw sample import. Only applies to bit depths of 16 or more. | |||
=== | === Device Chain Import === | ||
Applies to XRNT files. | |||
Applies to | |||
* '''Replace Existing Chain:''' When enabled, loading a device chain will completely erase all existing devices first. When disabled, the imported chain is appended. | |||
* '''Replace Existing Chain''' When enabled, loading a device chain will completely erase all existing devices first. When disabled, the imported chain is appended. | |||
=== '' | === MIDI Import ''(Renoise Only)'' === | ||
=== | Applies to MID or MIDI files. | ||
Applies to exported XRNI (Renoise Instrument files) and XRNS (Renoise Song | |||
* '''Create instruments:''' Create instruments based upon the instruments used in the MIDI file. When disabled, only notes and CC events are imported and so instruments have to be set up manually. | |||
* '''Create *Instr. MIDI Control devices:''' Create MIDI Control devices to import and send MIDI control change messages (e.g. modulation wheel). | |||
* '''Lines per pattern:''' Divide the imported MIDI song into patterns of the given length. | |||
* '''MIDI device:''' Choose the MIDI device for selecting the MIDI instruments from (and send output to). | |||
=== Song/Instrument/Sfz Export ''(Renoise Only)'' === | |||
Applies to exported XRNI (Renoise Instrument files) and XRNS (Renoise Song files). | |||
* '''Sample format:''' Select how samples are stored in Renoise song or instrument files. XRNI and XRNS files are regular zip files with a custom extension, so it is possible to open them with any tool which can use zip files (e.g. WinRar/WinZip on Windows, Stuff-it on MacOS) and extract all of the samples manually. ''"Flac"'' will result in smaller files and should be used by default. ''"Wav"'' files might be useful if you later want to extract the files and use them in other programs. | |||
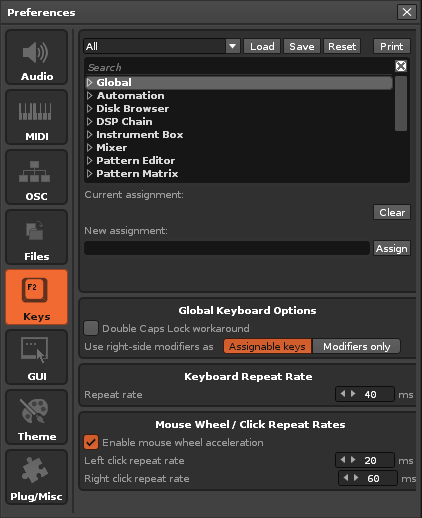
== Keys == | == Keys == | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:3.3_preferences-keys.png]] | ||
=== Keyboard Mapping List === | |||
All of the keyboard shortcuts in Renoise/Redux can be re-configured. Above the list you can choose the Focus of the mappings, which changes the part of the interface that the shortcuts apply to. Selecting ''"All"'' will give an overview of all existing keyboard shortcuts in Renoise/Redux, making it easier to search for a specific setting. | |||
There are many mappings which are not assigned by default, so if you need to create one that does not exist yet, take a look at the available mappings in the relevant section. To change or create a keyboard mapping, select the mapping in the list and click on the ''"New Assignment"'' box. Press the key combination you would like to use and then hit the 'Assign' button. If the given combination is already used somewhere else you will be warned of this. The new configuration will be saved automatically. | |||
=== Importing/Exporting Keyboard Mappings === | |||
* [[Image:3.0_preferences-keysload.png|text-bottom]] - Load a saved set of key-bindings. | |||
* [[Image:3.0_preferences-keyssave.png|text-bottom]] - Save a custom set of key-bindings. | |||
* [[Image:3.0_preferences-keysreset.png|text-bottom]] - Reset to the default key-bindings. | |||
* [[Image:3.0_preferences-keysprint.png|text-bottom]] - Display the current key-binding layout in your default browser in a print-friendly format. | |||
=== Global Keyboard Options === | |||
* '''Double Caps Lock workaround:''' If your Caps Lock key is not behaving as normal (requiring two presses, or entering two Note-Offs instead of one), then enable this option. | |||
* '''Use right-side modifiers as:''' Changes whether the right-side Control/Shift/Alt keys are to be used as modifiers (in combination with other keys, e.g. Ctrl + Z) or can be assigned functions on their own. | |||
=== Keyboard Repeat Rate === | |||
* '''Repeat Rate:''' Configure how fast key presses are repeated. | |||
=== Mouse Wheel/Click Repeat Rate === | |||
* '''Enable mouse wheel acceleration:''' Will make the use of the mouse wheel more sensitive. | |||
* '''Left-Click Repeat Rate:''' Set how fast changes to a value with a left-click will be repeated (e.g. increasing the BPM using the small arrows). | |||
* '''Right-Click Repeat Rate:''' Same as above, but for right mouse button clicks. | |||
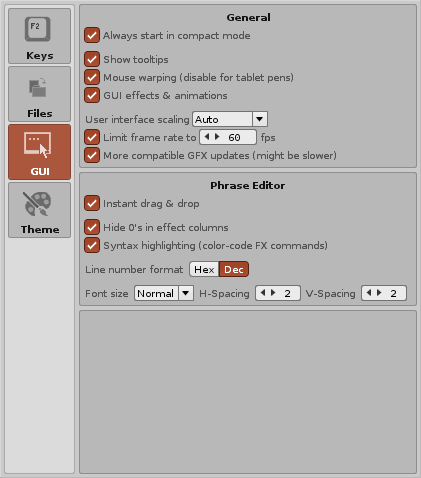
== GUI == | |||
[[Image:3.3_preferences-gui.png]] [[Image:dux1.1_preferences-gui.png]] | |||
The GUI options allow the customisation of the general display behaviour. | |||
=== Global / General === | |||
* '''Always start in compact mode:''' ''(Redux only)'' Toggle always starting in [[Redux_main_screen#Compact_Mode|compact mode]] when Redux is launched. | |||
* '''Show tooltips:''' Toggle the displaying of tooltips when the mouse pointer hovers over a significant part of the interface for a second. | |||
* '''Mouse warping (disable for tablet pens):''' Disable to increase usability for tablet pens. | |||
* '''GUI effects & animations:''' When enabled, animations will be used in some parts of the interface, e.g. smooth scrolling, fading of menus, transparency etc. Disable this option if you dislike them or are using a very slow computer. | |||
* '''Enable Retina HiDPI display support:''' ''(Mac only)'' Toggles [[HiDPI and UI Scaling|HiDPI]] support on/off. | |||
* '''User interface scaling:''' Can override the amount of scaling used by the default ‘Auto’ setting, which uses your main display’s DPI value, and instead uses a percentage chosen from 100-350%. This option can still be used to enlarge the Renoise GUI even if your display isn’t [[HiDPI and UI Scaling|HiDPI]], making it more comfortable to use on higher resolution screens. | |||
* '''Limit frame rate to:''' Set how fast the GUI will update itself. Lower values require less CPU power, while higher values result in a more responsive user interface. Disabling the frame rate will allow use of the necessary amount of CPU power to update the GUI as responsively as possible. | |||
* '''More compatible GFX updates (might be slower):''' ''(Windows only)'' Uses a possibly slower method of drawing the GUI with your graphics card. This option should be kept on unless it needs to be disabled to avoid problems with multi-monitor setups. | |||
* '''Enable Metal based GFX updates:''' ''(MacOS only)'' Enables Apple's Metal API for the Renoise UI instead of using CoreGraphics. This should result in a much smoother UI when your GFX cards supports Metal, and is enabled by default when Renoise detects a Retina screen on the first launch after installation. | |||
=== Pattern/Phrase Editor === | |||
* '''Single click to set cursor in edit mode:''' ''(Renoise only)'' This allows a single left-click in a pattern to move the cursor to that exact position when [[Recording_and_Editing_Notes#Edit_Mode|Edit Mode]] is on. When Edit Mode is off, it also allows a single left-click to move the cursor to that column without changing the pattern line. A double-click will always move the cursor to that exact position regardless of whether this option is enabled or not. | |||
* '''Instant drag & drop:''' When enabled, clicking upon a selected area in the Pattern Editor will instantly start to drag the selection. When disabled, you have to click and hold for a second to drag. | |||
* '''Hide 0s in effect columns:''' Hides 0s in the effect columns. | |||
* '''View multiple patterns continuously:''' ''(Renoise only)'' Show previous/next patterns at the edges of the current pattern. | |||
* '''Syntax highlighting (color-code FX commands):''' Highlights different types of [[Effect Commands]] with different colors. | |||
* '''Line number format:''' Use either decimal or [[Tracker_Interface#Hexadecimal|hexadecimal]] for the Pattern Editor line numbers. | |||
* '''Font size:''' Choose between four font sizes. | |||
* '''H-Spacing:''' The horizontal spacing between individual letters and numbers. | |||
* '''V-Spacing:''' The vertical spacing between lines. | |||
=== Pattern Sequencer ''(Renoise only)'' === | |||
* '''Separate edit & play positions (with pattern follow disabled):''' When enabled, the sequencer's playback position will be detached from the edit position when [[Transport Panel|Pattern Follow]] is disabled. | |||
=== Envelopes ''(Renoise only)'' === | |||
* '''Single click to create new points (hold Shift to select):''' When enabled, reverts to the old behaviour of a single left-click to create new points in envelopes. | |||
=== Scopes ''(Renoise only)'' === | |||
* '''Show track names:''' Deactivating this will remove the track names from the Scopes and display their track numbers instead. | |||
* '''Show track color blends:''' Show the [[Pattern_Editor#Changing_Track_Colors|background colors selected for each track]] as the background color of its [[Scopes#Track_Scopes|Track Scope]]. | |||
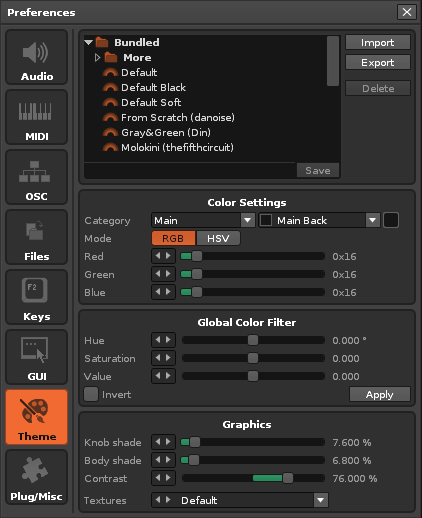
== Theme == | |||
[[Image:3.3_preferences-theme.png]] | |||
=== Theme Files === | |||
There are four different options for handling Theme files (.xrnc) here and they can also be Imported/Exported in the [[Disk Browser]]. | |||
* Import a Theme file. To store this within Renoise/Redux for future use, be sure to also Save it. | |||
* Export the current colour settings to a file. | |||
* Delete the selected user-created (non-bundled) Theme. | |||
* Save the current colour settings as a user-created Theme. Before pressing Save, enter the desired name into the text field, finishing with ''"Enter"''. | |||
=== Color Settings === | |||
Change individual colour settings. Colours are organized into multiple categories. | |||
=== Global Color Filter === | |||
Adjust all colour settings at once by applying Hue, Saturation or Value changes to them. | |||
=== | === Graphics === | ||
Change the texture set and bevel amounts that are used for the current Theme. | |||
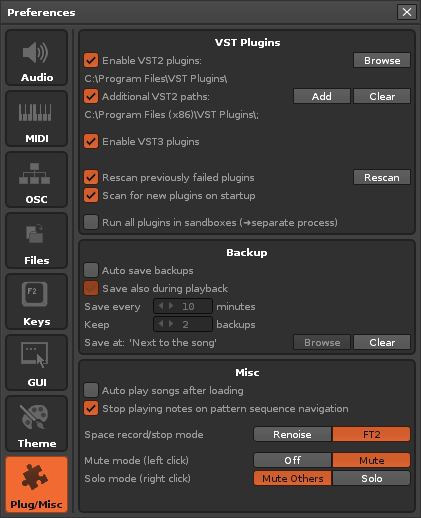
== | == Plugins/Misc == | ||
[[Image:3.4_preferences-plugmisc.png]] | |||
== | === Audio Unit Plugins (MacOS only) === | ||
* Enable the use of Audio Unit plugins in Renoise. | |||
=== LADSPA Plugins (Linux only) === | |||
* | * Enable the use of LADSPA plugins in Renoise. | ||
=== VST2 Plugins (Windows, Mac & Linux) === | |||
* Enable the use of VST2 plugins in Renoise and choose the initial folder where Renoise will scan for plugin files. | |||
* Enable and choose a second folder ''(Linux)'' or multiple folders ''(Win & MacOS)'' where Renoise will scan for plugin files. | |||
== | === VST3 Plugins (Windows, Mac & Linux) === | ||
* Enable the use of VST3 plugins in Renoise. Please note that, regardless of where you install other files, the actual VST3 files '''''must''''' be located in [https://helpcenter.steinberg.de/hc/en-us/articles/115000177084-VST-plug-in-locations-on-Windows the default directory] or they will not be detected. | |||
=== Plugins General (Windows, Mac & Linux) === | |||
* '''Rescan previously failed plugins:''' When hitting the ''"Rescan"'' button, Renoise will try to open plugins that failed to open in previous scans. Plugins which caused a crash upon scanning are never rescanned though, unless you delete the VST cache files in the Renoise preferences folder. When this option is disabled, hitting the ''"Rescan"'' button will only look for new plugins. | |||
* '''Rescan:''' Rescan for new plugins or try to rescan previously failed plugins (see above). | |||
* '''Scan for new plugins on startup:''' By default, Renoise will always start scanning for new plugins when launched. If you have a large amount of plugins installed then disabling this option can vastly improve startup time. If disabled, then after installing new plugins you will have manually scan for them with the ''"Rescan"'' button, as described above. | |||
* '''Run all plugins in sandboxes (➜separate process):''' When enabled, plugins will be started in their own process, preventing bugged ones from crashing Renoise. | |||
== | === Backup === | ||
* ''' | * '''Auto save backups:''' When enabled, Renoise will periodically save backups of your current song. For existing songs, the backups are saved into a new folder named after the song. For 'Untitled' songs, the backups will be saved into the Renoise preferences folder. | ||
* '''Save also during playing:''' When enabled, backups will be saved as songs are playing, which could possibly cause interruptions in the audio. If you want to avoid this while composing, disable this option. | |||
* '''Save every xx minutes:''' How often backups will be saved. | |||
* '''Keep xx backups:''' Specify how many revisions of the backups will be kept. | |||
* '''Save at:''' Instead of being saved next to the original song files, you can specify a folder to place the backups. | |||
=== Misc === | |||
* ''' | * '''Auto play songs after loading:''' When enabled, Renoise will automatically start playback as soon as a song is loaded. | ||
* '''Stop playing notes on pattern sequence navigation:''' When navigating around in the [[Pattern Sequencer]], Renoise will stop all playing notes and then skip over to the new pattern to continue playback, avoiding 'hanging' notes. You can disable this behaviour here. | |||
* '''Space record/stop mode''' | |||
** '''Renoise:''' Use the space key to start/stop playing. | |||
** '''FT2:''' Use the space key to stop the song or toggle [[Recording_and_Editing_Notes#Edit_Mode|Edit Mode]] if the song is already stopped. | |||
* '''Mute mode (left click):''' | |||
** '''Off:''' ''(Soft Mute)'' Muting a track will act as a [[Playing_Notes_with_the_Computer_Keyboard#Note_Off|Note-Off]] event for any instruments playing in the track, so you may hear them carry on until finished. New notes and [[Effect Commands]] playing in the track will not be triggered while the Mute is active. | |||
** '''Mute:''' ''(Mixer Mute)'' Muting a track will immediately silence all audio. New notes and [[Effect Commands]] playing in the track will still be triggered while the Mute is active, so un-muting will instantly bring back all audio. | |||
* '''Solo mode (right click):''' | |||
*** '''Mute''' | ** '''Mute Others:''' Solo-ing a track will cause all other tracks to be muted. Unsolo-ing will un-mute all other tracks. | ||
** '''Solo:''' Solo-ing and unsolo-ing track will retain the mute states of all other tracks. | |||
Latest revision as of 17:08, 21 March 2022
Preferences
The Renoise Preferences panel lets you set various general options for the program, such as soundcard settings, MIDI device settings, how files are loaded/saved etc. These settings need to be set only once and will be applied to all songs and sounds you create with Renoise.
To open the Preferences panel, choose "Edit -> Preferences..." from the main menu (Windows + Linux). On the Mac, choose "Renoise -> Preferences...".
When setting up Renoise for the first time, you should only need to tweak the options in the Audio and MIDI tabs. The rest of the default options should be sufficient until you are more familiar with Renoise. The Setting Up Audio Devices and Setting Up MIDI Devices sections of the manual can help you with the initial setup.
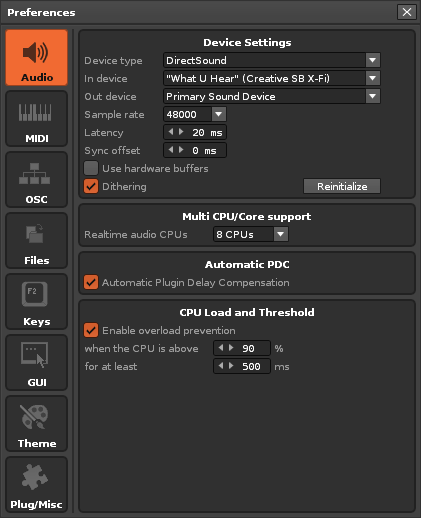
Audio
Device Settings (Windows)
- Device Type: Determines the sound driver that Renoise will use. On Windows you will have the choice between DirectSound, WASAPI and ASIO. If available, ASIO is highly recommended as it provides better timing with MIDI instruments and lower latencies in general.
- In Device: (DirectSound only) If you have multiple soundcards installed, you will be able to select the one you want to use with Renoise here. Choose "Primary Device" to use the system's default.
- Out Device: (DirectSound only) If you have multiple soundcards installed, you will be able to select the one you want to use with Renoise here. Choose "Primary Device" to use the system's default.
- Sample Rate: Select the Sample Rate for playback. All internal audio processing in Renoise will be done at this rate. The higher the Sample Rate, the more detailed the results will be, but also the more CPU power will be used.
- Latency: (DirectSound only) Set the buffer size affecting overall latency. Higher numbers will reduce the possibility of crackling sound at high CPU usage, but will also cause more latency (the time it takes the sound from Renoise to reach an output and be heard).
- Sync offset: A custom offset applied when synchronizing audio playback to an external source such Ableton Link peers. It is only necessary to set this if Renoise cannot reliably detect the actual output latency of the audio device.
- Use hardware buffers: (DirectSound only) This option may speed up playback processing a bit, but only some soundcards support this. If you enable this option, then experiment with recording in the Sampler before deciding to use it permanently, as it may cause issues. If you experience strange results then disable this function.
- Limit to stereo in/out: (ASIO only) If you have a multi-IO soundcard, you can disable all inputs and outputs except for the main stereo pair. This may lead to better performance when you don't need the other channels.
- Dithering: Apply dithering to the audio stream when the soundcard uses a bit depth of 8 or 16 bit. 24 and 32 bit audio is never dithered.
- Control Panel: (ASIO only) Opens the ASIO driver's control panel where you can configure your soundcard in more detail.
- Reinitialize: Shut down and then reopen all connections to the soundcard/driver. May be useful for troubleshooting.
Device Settings (MacOS)
- In Device: If you have multiple soundcards installed, you will be able to select the one you want to use with Renoise here.
- Out Device: If you have multiple soundcards installed, you will be able to select the one you want to use with Renoise here.
- Sample Rate: Select the Sample Rate for playback. All internal audio processing in Renoise will be done at this rate. The higher the Sample Rate, the more detailed the results will be, but also the more CPU power will be used.
- Latency: Set the buffer size affecting overall latency. Higher numbers will reduce the possibility of crackling sound at high CPU usage, but will also cause more latency (the time it takes the sound from Renoise to reach an output and be heard).
- Dithering: Apply dithering to the audio stream when the soundcard uses a bit depth of 8 or 16 bit. 24 and 32 bit audio is never dithered.
- Reinitialize: Shut down and then reopen all connections to the soundcard/driver. May be useful for troubleshooting.
Device Settings (Linux)
Setting up Linux for fast and reliable audio usage can be quite complex, depending on the distribution you are using. For general questions and FAQs regarding sound output on Linux, take a look at the Linux FAQ.
- Device Type: Determines the sound driver that Renoise will use. On Linux you have the choice between ALSA and Jack. ALSA will be available on all setups. Jack is more advanced, but also harder to set up and may have to be installed manually. Jack is highly recommended though, because it allows you to use several Jack based audio applications at once with the ability to route audio between them.
- In Device:
- ALSA: If you have multiple soundcards installed, you will be able to select the one you want to use with Renoise here.
- Jack: Select the number of input pairs you would like to pass over to Jack.
- Out Device:
- ALSA: If you have multiple soundcards installed, you will be able to select the one you want to use with Renoise here.
- Jack: Select the number of output pairs you would like to pass over to Jack.
- Sample Rate: (ALSA only) Select the Sample Rate for playback. All internal audio processing in Renoise will be done at this rate. The higher the Sample Rate, the more detailed the results will be, but also the more CPU power will be used.
- Buffer Size: (ALSA only) The base buffer size that will be used for audio processing in Renoise. Higher numbers will reduce the possibility of crackling sound at high CPU usage, but will also cause more latency (the time it takes the sound from Renoise to reach an output and be heard).
- Periods/Buffer: (ALSA only) How many "Buffer Sizes" will be used. The final latency for ALSA playback is: Periods/Buffer * Buffer Size. Some drivers need three buffers to work reliably, while others need only two. If you hear crackling output from Renoise, try changing this value or the setting for "In Device".
- Use realtime priority: (ALSA only) On most 'out of the box' Linux systems, applications are not allowed to execute realtime performance critical tasks. They are needed for realtime audio processing though, so they should be enabled when possible. Please see the Linux FAQ for more info about this topic. If you cannot configure your system to allow realtime tasks, then you can disable Renoise from trying with this option.
- Enable Transport Support: (Jack only) Send and receive time and transport information to/from other applications that are running with Jack. This is only useful to sync multiple audio applications together. If you are only running Renoise, this option should be disabled.
- Dithering: Apply dithering to the audio stream when the soundcard uses a bit depth of 8 or 16 bit. 24 and 32 bit audio is never dithered.
- Reinitialize: Shut down and then reopen all connections to the soundcard/driver. May be useful for troubleshooting.
Multi CPU/Core support
- Realtime Audio CPUs: If you have a processor with multiple CPUs or cores, you can adjust how Renoise makes use of them for real-time audio processing. By default, all cores are used, which is highly recommended.
Automatic PDC
- Automatic Plugin Delay Compensation: This automatically compensates all delays that some Renoise internal effects and VST/AU plugins introduce. Used to ensure all tracks and instruments are played back in sync. If you are troubleshooting, you may want to temporarily disable this option. The Automatic PDC can also be quickly toggled from the Options menu.
CPU Load and Threshold
- When the CPU is above, For at least: - When the conditions are fulfilled, Renoise executes Panic (instantly stops all playback). This option prevents very high CPU loads from freezing your computer.
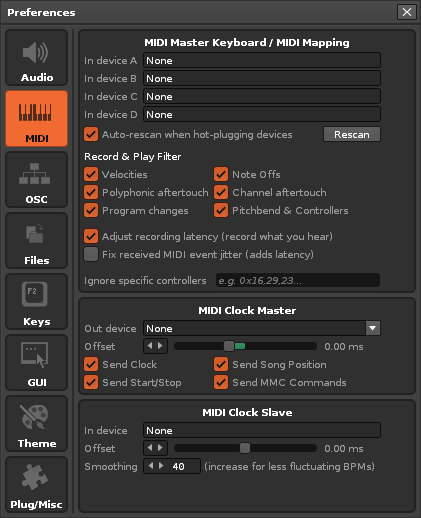
MIDI
MIDI Master Keyboard/Mapping
- In Device A/B/C/D: Select up to four devices to be used for general MIDI input in Renoise (Recording and Editing Notes) and for MIDI remote control (MIDI Mapping).
- Auto-rescan when hot-plugging devices: When enabled and devices are hot-plugged, rescan for MIDI devices in Renoise too, so they can be immediately used.
- Rescan: Manually rescan MIDI devices.
- Record and Play Filters: Toggle the input and recording of specific MIDI messages for Renoise. This only applies to recording into patterns and real-time playback.
- Adjust recording latency: Will automatically compensate for MIDI latencies, so that you record what you hear, not what you play.
- Fix received MIDI event jitter: Shifts received MIDI events slightly forward in time to fix MIDI transmission jitter. Stabilizes MIDI input, but also delays input by an entire audio buffer.
- Ignore specific controllers: Explicitly prevent certain MIDI Control Change messages from being received and recorded. You can enter a list of CC numbers here, separated by commas.
MIDI Clock Master
- Out Device: Set a MIDI device that Renoise will send MIDI Clock data to.
- Offset: Manually shift all messages sent out to the devices by the given amount. This can be useful to manually compensate additional latencies that external devices introduce (audio latency is always automatically compensated by Renoise). Please note that the smallest possible negative latency is limited to the current latency of your soundcard. If you need further negative latency, you can increase your audio latency in the Audio Preferences.
- Send clock: Include sending MIDI Clock pulse messages.
- Send start/stop: Include sending MIDI Clock start/stop messages.
- Send song position pointers: Include sending MIDI Clock song position messages.
- Send MIDI Machine Control (MMC): In addition to the MIDI clock, also send MMC sysex messages to sync external devices to Renoise.
MIDI Clock Slave
- In-Device: Select the MIDI Device that Renoise will use to receive MIDI Clock messages. When enabled, you can slave Renoise to a MIDI Clock master (a device which sends MIDI Clock messages). As soon as a MIDI Clock device is set, you will see a new option in the Transport Panel. This option must be enabled to activate sync from external devices and so can also be used to toggle sync quickly without having to constantly open the Preferences.
- Offset: Manually shift incoming timing information by the given amount. This can be useful to manually compensate extra latencies that the external MIDI Clock devices introduce (audio latency is always automatically compensated by Renoise). Since Renoise can't predict the future, a negative latency setting will lead to the offset being gradually shifted to its requested position after playback starts.
- Smoothing: MIDI messages often only have very rough timing, so the beat clock messages transferred from a MIDI Clock master to Renoise may be imperfect. Depending on how precise the incoming MIDI clock stream is, you can use this option to set how fast Renoise should react to changes from the MIDI Clock master. The higher the Smoothing value, the more stable the sync will be, but the slower Renoise will react to 'real' BPM changes from the master. Try playing around with the Smoothing to find a good value for your setup.
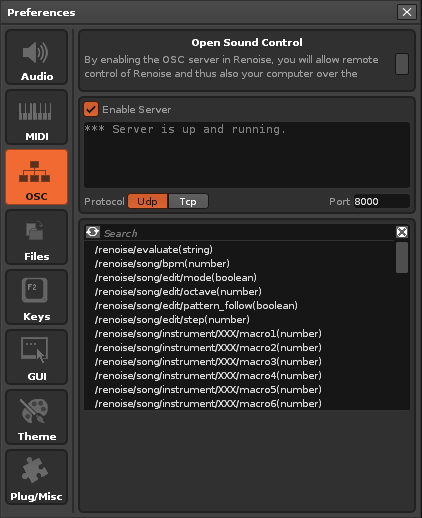
OSC
Server
The server is enabled with the checkbox near the top, though note that you are opening up a port that is listening for incoming traffic. If you are not planned to use OSC messaging between Renoise and another OSC client, it is advisable to leave the OSC server disabled. Beneath the checkbox is the messaging log window, which shows details of any incoming data and provides feedback on whether outgoing data has been sent correctly or otherwise.
- Protocol: Choose from UDP (for local network and anything with a fast, stable connection) or TCP (for remote networks requiring more secure feedback on delivery status).
- Port: The port number, which by default is 8000, but can be changed to any desired port.
Renoise OSC Messaging Protocols
Renoise provides four sub-trees in its root messaging tree of /renoise/:
- evaluate - Send Lua strings for Renoise to evaluate.
- song - Send song specific triggers to activate.
- transport - Send transport specific triggers to activate.
- trigger - Send note specific triggers to activate.
For full details of using OSC within Renoise, please refer to its section of the manual.
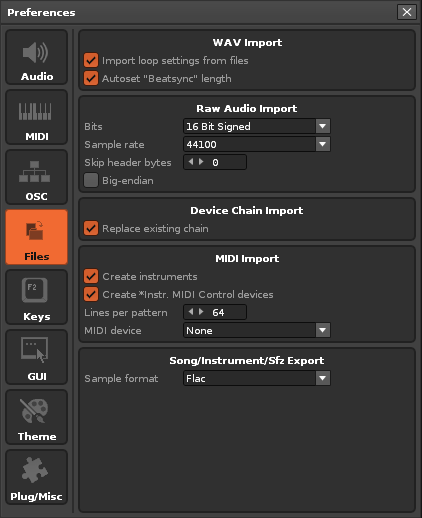
Files
Note: All import options mentioned below can also be quickly accessed in the Disk Browser by right-clicking the file, then choosing "Load File with Options..."
WAV Import
Applies to WAV, FLAC, AIF, OGG and MP3 files.
- Import loop settings from files: Enables the importing of loop settings that are saved along with WAV, FLAC and AIF files.
- Autoset 'Beatsync' length: When loading samples, a good Beatsync value will be automatically estimated in the Sample Properties, overwriting previous values. If you don't want this to happen, disable it here.
Raw Audio Import
Applies to any non-audio files that are forced to be loaded as audio. See Importing Raw Audio for more details.
- Bits: Bit-rate that will be applied to the imported raw sample.
- Sample Rate: Sample rate of raw samples.
- Skip header bytes: Will skip the specified number of bytes and not treat them as audio data.
- Big Endian: Select the byte order that will be used for the raw sample import. Only applies to bit depths of 16 or more.
Device Chain Import
Applies to XRNT files.
- Replace Existing Chain: When enabled, loading a device chain will completely erase all existing devices first. When disabled, the imported chain is appended.
MIDI Import (Renoise Only)
Applies to MID or MIDI files.
- Create instruments: Create instruments based upon the instruments used in the MIDI file. When disabled, only notes and CC events are imported and so instruments have to be set up manually.
- Create *Instr. MIDI Control devices: Create MIDI Control devices to import and send MIDI control change messages (e.g. modulation wheel).
- Lines per pattern: Divide the imported MIDI song into patterns of the given length.
- MIDI device: Choose the MIDI device for selecting the MIDI instruments from (and send output to).
Song/Instrument/Sfz Export (Renoise Only)
Applies to exported XRNI (Renoise Instrument files) and XRNS (Renoise Song files).
- Sample format: Select how samples are stored in Renoise song or instrument files. XRNI and XRNS files are regular zip files with a custom extension, so it is possible to open them with any tool which can use zip files (e.g. WinRar/WinZip on Windows, Stuff-it on MacOS) and extract all of the samples manually. "Flac" will result in smaller files and should be used by default. "Wav" files might be useful if you later want to extract the files and use them in other programs.
Keys
Keyboard Mapping List
All of the keyboard shortcuts in Renoise/Redux can be re-configured. Above the list you can choose the Focus of the mappings, which changes the part of the interface that the shortcuts apply to. Selecting "All" will give an overview of all existing keyboard shortcuts in Renoise/Redux, making it easier to search for a specific setting.
There are many mappings which are not assigned by default, so if you need to create one that does not exist yet, take a look at the available mappings in the relevant section. To change or create a keyboard mapping, select the mapping in the list and click on the "New Assignment" box. Press the key combination you would like to use and then hit the 'Assign' button. If the given combination is already used somewhere else you will be warned of this. The new configuration will be saved automatically.
Importing/Exporting Keyboard Mappings
 - Load a saved set of key-bindings.
- Load a saved set of key-bindings. - Save a custom set of key-bindings.
- Save a custom set of key-bindings. - Reset to the default key-bindings.
- Reset to the default key-bindings. - Display the current key-binding layout in your default browser in a print-friendly format.
- Display the current key-binding layout in your default browser in a print-friendly format.
Global Keyboard Options
- Double Caps Lock workaround: If your Caps Lock key is not behaving as normal (requiring two presses, or entering two Note-Offs instead of one), then enable this option.
- Use right-side modifiers as: Changes whether the right-side Control/Shift/Alt keys are to be used as modifiers (in combination with other keys, e.g. Ctrl + Z) or can be assigned functions on their own.
Keyboard Repeat Rate
- Repeat Rate: Configure how fast key presses are repeated.
Mouse Wheel/Click Repeat Rate
- Enable mouse wheel acceleration: Will make the use of the mouse wheel more sensitive.
- Left-Click Repeat Rate: Set how fast changes to a value with a left-click will be repeated (e.g. increasing the BPM using the small arrows).
- Right-Click Repeat Rate: Same as above, but for right mouse button clicks.
GUI
The GUI options allow the customisation of the general display behaviour.
Global / General
- Always start in compact mode: (Redux only) Toggle always starting in compact mode when Redux is launched.
- Show tooltips: Toggle the displaying of tooltips when the mouse pointer hovers over a significant part of the interface for a second.
- Mouse warping (disable for tablet pens): Disable to increase usability for tablet pens.
- GUI effects & animations: When enabled, animations will be used in some parts of the interface, e.g. smooth scrolling, fading of menus, transparency etc. Disable this option if you dislike them or are using a very slow computer.
- Enable Retina HiDPI display support: (Mac only) Toggles HiDPI support on/off.
- User interface scaling: Can override the amount of scaling used by the default ‘Auto’ setting, which uses your main display’s DPI value, and instead uses a percentage chosen from 100-350%. This option can still be used to enlarge the Renoise GUI even if your display isn’t HiDPI, making it more comfortable to use on higher resolution screens.
- Limit frame rate to: Set how fast the GUI will update itself. Lower values require less CPU power, while higher values result in a more responsive user interface. Disabling the frame rate will allow use of the necessary amount of CPU power to update the GUI as responsively as possible.
- More compatible GFX updates (might be slower): (Windows only) Uses a possibly slower method of drawing the GUI with your graphics card. This option should be kept on unless it needs to be disabled to avoid problems with multi-monitor setups.
- Enable Metal based GFX updates: (MacOS only) Enables Apple's Metal API for the Renoise UI instead of using CoreGraphics. This should result in a much smoother UI when your GFX cards supports Metal, and is enabled by default when Renoise detects a Retina screen on the first launch after installation.
Pattern/Phrase Editor
- Single click to set cursor in edit mode: (Renoise only) This allows a single left-click in a pattern to move the cursor to that exact position when Edit Mode is on. When Edit Mode is off, it also allows a single left-click to move the cursor to that column without changing the pattern line. A double-click will always move the cursor to that exact position regardless of whether this option is enabled or not.
- Instant drag & drop: When enabled, clicking upon a selected area in the Pattern Editor will instantly start to drag the selection. When disabled, you have to click and hold for a second to drag.
- Hide 0s in effect columns: Hides 0s in the effect columns.
- View multiple patterns continuously: (Renoise only) Show previous/next patterns at the edges of the current pattern.
- Syntax highlighting (color-code FX commands): Highlights different types of Effect Commands with different colors.
- Line number format: Use either decimal or hexadecimal for the Pattern Editor line numbers.
- Font size: Choose between four font sizes.
- H-Spacing: The horizontal spacing between individual letters and numbers.
- V-Spacing: The vertical spacing between lines.
Pattern Sequencer (Renoise only)
- Separate edit & play positions (with pattern follow disabled): When enabled, the sequencer's playback position will be detached from the edit position when Pattern Follow is disabled.
Envelopes (Renoise only)
- Single click to create new points (hold Shift to select): When enabled, reverts to the old behaviour of a single left-click to create new points in envelopes.
Scopes (Renoise only)
- Show track names: Deactivating this will remove the track names from the Scopes and display their track numbers instead.
- Show track color blends: Show the background colors selected for each track as the background color of its Track Scope.
Theme
Theme Files
There are four different options for handling Theme files (.xrnc) here and they can also be Imported/Exported in the Disk Browser.
- Import a Theme file. To store this within Renoise/Redux for future use, be sure to also Save it.
- Export the current colour settings to a file.
- Delete the selected user-created (non-bundled) Theme.
- Save the current colour settings as a user-created Theme. Before pressing Save, enter the desired name into the text field, finishing with "Enter".
Color Settings
Change individual colour settings. Colours are organized into multiple categories.
Global Color Filter
Adjust all colour settings at once by applying Hue, Saturation or Value changes to them.
Graphics
Change the texture set and bevel amounts that are used for the current Theme.
Plugins/Misc
Audio Unit Plugins (MacOS only)
- Enable the use of Audio Unit plugins in Renoise.
LADSPA Plugins (Linux only)
- Enable the use of LADSPA plugins in Renoise.
VST2 Plugins (Windows, Mac & Linux)
- Enable the use of VST2 plugins in Renoise and choose the initial folder where Renoise will scan for plugin files.
- Enable and choose a second folder (Linux) or multiple folders (Win & MacOS) where Renoise will scan for plugin files.
VST3 Plugins (Windows, Mac & Linux)
- Enable the use of VST3 plugins in Renoise. Please note that, regardless of where you install other files, the actual VST3 files must be located in the default directory or they will not be detected.
Plugins General (Windows, Mac & Linux)
- Rescan previously failed plugins: When hitting the "Rescan" button, Renoise will try to open plugins that failed to open in previous scans. Plugins which caused a crash upon scanning are never rescanned though, unless you delete the VST cache files in the Renoise preferences folder. When this option is disabled, hitting the "Rescan" button will only look for new plugins.
- Rescan: Rescan for new plugins or try to rescan previously failed plugins (see above).
- Scan for new plugins on startup: By default, Renoise will always start scanning for new plugins when launched. If you have a large amount of plugins installed then disabling this option can vastly improve startup time. If disabled, then after installing new plugins you will have manually scan for them with the "Rescan" button, as described above.
- Run all plugins in sandboxes (➜separate process): When enabled, plugins will be started in their own process, preventing bugged ones from crashing Renoise.
Backup
- Auto save backups: When enabled, Renoise will periodically save backups of your current song. For existing songs, the backups are saved into a new folder named after the song. For 'Untitled' songs, the backups will be saved into the Renoise preferences folder.
- Save also during playing: When enabled, backups will be saved as songs are playing, which could possibly cause interruptions in the audio. If you want to avoid this while composing, disable this option.
- Save every xx minutes: How often backups will be saved.
- Keep xx backups: Specify how many revisions of the backups will be kept.
- Save at: Instead of being saved next to the original song files, you can specify a folder to place the backups.
Misc
- Auto play songs after loading: When enabled, Renoise will automatically start playback as soon as a song is loaded.
- Stop playing notes on pattern sequence navigation: When navigating around in the Pattern Sequencer, Renoise will stop all playing notes and then skip over to the new pattern to continue playback, avoiding 'hanging' notes. You can disable this behaviour here.
- Space record/stop mode
- Renoise: Use the space key to start/stop playing.
- FT2: Use the space key to stop the song or toggle Edit Mode if the song is already stopped.
- Mute mode (left click):
- Off: (Soft Mute) Muting a track will act as a Note-Off event for any instruments playing in the track, so you may hear them carry on until finished. New notes and Effect Commands playing in the track will not be triggered while the Mute is active.
- Mute: (Mixer Mute) Muting a track will immediately silence all audio. New notes and Effect Commands playing in the track will still be triggered while the Mute is active, so un-muting will instantly bring back all audio.
- Solo mode (right click):
- Mute Others: Solo-ing a track will cause all other tracks to be muted. Unsolo-ing will un-mute all other tracks.
- Solo: Solo-ing and unsolo-ing track will retain the mute states of all other tracks.