Introduction To Redux
Main Screen
This introduction will familiarise you with the main components of both Renoise and Redux interfaces, as well as explain their basic functions.
Renoise Main Screen Overview
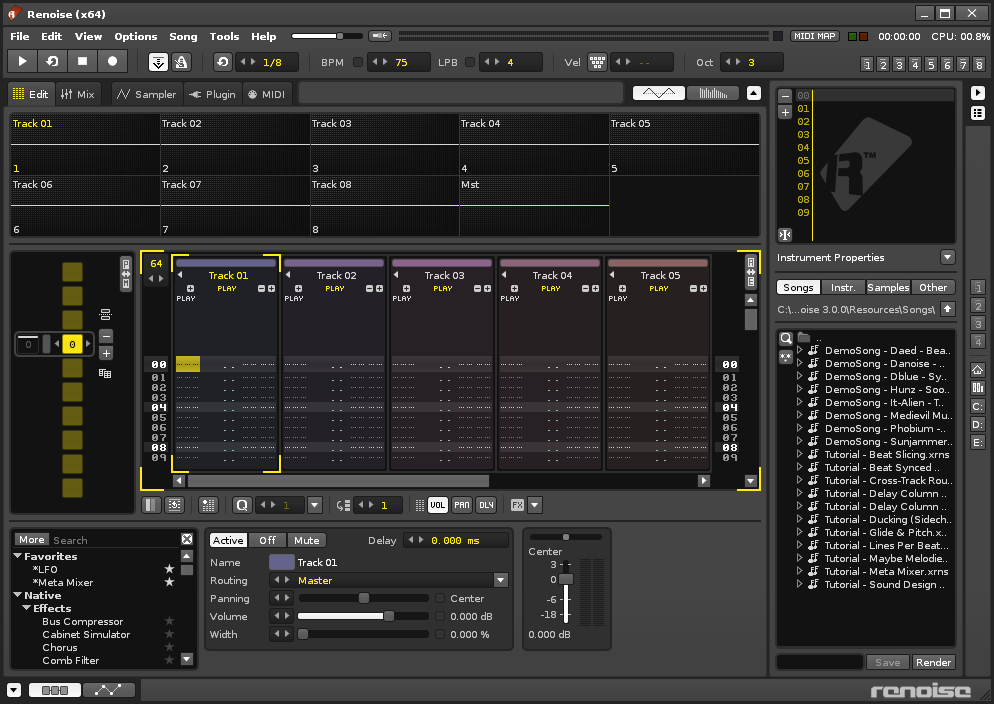
Renoise is significantly different from most other music creation packages and consequently it also looks different. When you load Renoise for the first time you will be presented with something similar to this:
Now we will briefly go through the main areas of the Renoise interface. Note the links in red, which you can click on for more detailed information about the various components.
Upper Status Bar
Located at the very top of the interface is the Upper Status Bar:
The left section of the status bar offers a variety of menu options. To the right of this is the Master volume slider which controls the overall volume of the song. Next is the button to auto adjust the Master volume level and avoid clipping (the volume is automatically lowered when clipping occurs). Further right is the VU meter showing the current Master volume level, followed by the MIDI controls (MIDI Mapping button, MIDI I/O LEDs), Song Timer and the current CPU usage.
Global Song Control
Just below the Upper Status Bar on the left-hand side are the basic Transport Panel controls.
From here you can start/stop the song and access basic editing features such as Edit Mode (record) and the metronome.
Song Visualisation
Below the Transport Panel are the Scopes.
The various Scopes help you to visually analyse the song.
Loading & Saving Files
At the bottom right corner of the interface is the Disk Browser.
Using the Disk Browser you can load or save songs, instruments, samples, effect chains etc. Upon first loading Renoise you will see a list of demo songs here. Double click on a song to load it, then press play to see and hear Renoise in action.
Selecting Instruments
Just above the Disk Browser is the Instrument Selector.
The Instrument Selector allows you to choose the instrument that you wish to play or record with, using either the computer keyboard or an external MIDI keyboard. Also, VST/AU or external MIDI instruments will appear in this section when they are loaded.
Creating & Editing Instruments
An Instrument in Renoise may be one or any combination of samples, plugins and MIDI, and each type can be created or edited by selecting the appropriate tab from the top left of the Renoise interface.
GUI presets
Directly above the Instrument Selector are a set of eight global preset buttons used to switch between various sections of the interface and are accessed by either clicking on them or pressing F1 - F8 on the keyboard. Renoise comes with eight presets already stored by default.
Sequencing Patterns
Located at the far left of the screen is the Pattern Sequencer.
Renoise uses a sequence of patterns to arrange the structure of a song and the Pattern Sequencer is used to create, copy and organise your patterns.
Creating Patterns
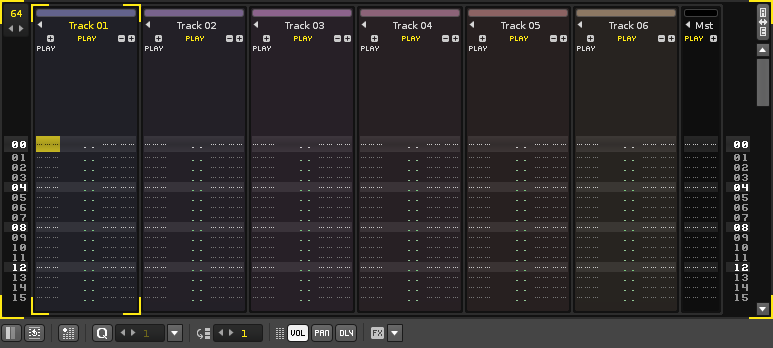
To the right of the Pattern Sequencer and occupying the main central space is the Pattern Editor.
This is the main tool for composing and editing within Renoise. Although it may look intimidating to beginners, the method of adding/recording notes into tracks using the Pattern Editor is actually incredibly simple.
Applying Effects
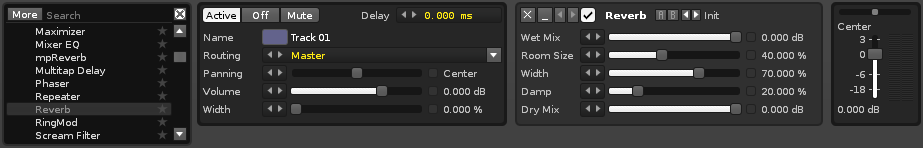
Beneath the central area is the panel for Track Effects:
This displays and controls all of the effects that are being applied to the current track (the track which the cursor is in). Besides the typical Audio Effects (Renoise/VST/AU/LADSPA) you can also assign Routing Devices to send/receive audio, and Meta Devices such as LFOs that do not affect audio, but are instead used to alter parameters and automation.
Lower Status Bar
Finally, at the very bottom is the Lower Status Bar.
The icons at the left allow you switch between the Track Effects and Graphical Automation panels or hide them completely. At significant points, Renoise will display information regarding its status and current operations here. If you wish to see the Welcome dialog box again, click on the Renoise logo at the right.
Redux Main Screen Overview
When launched, Redux will be in Compact Mode, which has been designed to take up minimal screen space while still providing access to essential features. Note that the Macros and the Phrase Bank/Trigger Mode will also be shown in Compact Mode when working with a preset that contains macros or phrases.
The full Redux interface is opened by clicking on the Editor button at the top-left.
The extra options available to you in this mode are almost identical to those in the Sampler section of Renoise. The plugin window can be resized by click-dragging its lower right corner.
At significant points, the Lower Status Bar will display information regarding the status and current operations of Redux.
Guide Yourself Through the Interface: Tooltips
As you are using Renoise watch out for Tooltips, which can be seen by hovering the mouse pointer over a button or part of the interface for a second. Almost every button in Renoise will provide you with a small tip about its function.
Renoise Work-flow: Learning the Keys
While Renoise supports drag'n'drop and mouse gestures, it is primarily a keyboard-based application. As such, there are keyboard shortcuts for practically every function. To view the available shortcuts, select "Help->List Keyboard Shortcuts..." from the Upper Status Bar. If you are interested in a shortcut specific to an interface area, you can right-click to open a context menu. Finally, the keyboard shortcuts can also be customised in the "Edit->Preferences->Keys" menu.
A list of most important shortcuts can also be found in the Keyboard Shortcuts section in this manual.